1. Introduction
Genetic evaluations are tools for the objective selection of sires that allow achieving genetic progress in production animals. In Uruguay, the number of herds and animals participating in genetic evaluations has grown steadily since the first published ones in 1993. Uruguay's Limousin Breeder Society, the Veterinary College, and the National Institute of Agricultural Research (sclu, fvet and inia, by their Spanish acronyms) have carried out the genetic evaluation of the breed in Uruguay since 2012. The objective is to achieve a population genetic evaluation, for which it is necessary to have the identification of the environmental factors that affect the evaluated characteristics, the genetic parameters estimated for the population, and the acceptable connectedness levels between the participating herds.
Genetic evaluations predict the genetic merit of an animal, based on its phenotype and/or that of its relatives. Therefore, it must be corrected by known factors that influence its expression, such as non-genetic or environmental effects1. According to Cardellino and Rovira2, the environment represents those external conditions that affect the reproduction, production, and composition of the cattle carcass, being its influence dependent on the analyzed characteristic. The adequate definition of contemporary groups (cg) is key to correct by environmental effects in a genetic evaluation3, and they were defined by Cundiff and others1 as the groups of animals of the same breed, sex and who have similar ages and management.
It is necessary to confirm the connectedness between herds, because it allows comparing animals in different productive environments and making precise comparisons of the breeding values of the candidates for selection4, thus increasing the intensity of selection and therefore the genetic progress. The easiest way to achieve connectedness within cg is through the use of reference animals, which have progeny with productive records in more than one herd and/or year. The offspring of a sire will share the same genetic information, regardless of the environment they are in5. There are two main methods for estimating connectedness, firstly, qualitative methods that identify only connected and disconnected groups, and secondly, quantitative methods that determine the degree of connectivity between herds. According to Magaña and others6, the latter are mostly based on the accuracy of differences in breeding values between two individuals and is expressed as the prediction error variance of the differences (pevd). According to Kennedy and Trus7, the most appropriate measure of connectivity is the average pevd of breeding values of animals from different herds. As there is a large number of animals in genetic evaluations, this measure must consider all pairs of individuals between herds, which makes it too complex for use. Mathur and others8 proposed an alternative measure of connectivity, which implies the measurement of the connectivity ranking (cr), defined as the correlation between the estimates of the herd effects or cg.
The objectives of this study are to determine the most relevant fixed environmental effects, and to estimate the connectedness rating between herds for the future population genetic evaluation of the Limousin breed in Uruguay.
2. Material and Methods
2.1 Data
The productive and genealogical records used come from the Limousin genetic evaluation database of the sclu-fvet-inia agreement.
The analyzed characteristics were weight at birth (wb), weight at weaning (ww), weight at 18 months (W18), ribeye area (rea) and rib fat thickness (rft) of bulls and heifers born between 2012 and 2016, belonging to four herds.
The data edition consisted of eliminating animals without date of birth and animals that received management based on natural field + ration, or pasture + ration. In turn, outlier records (less than 0.5% of the data) for W18 (>510 kg) and rib fat thickness (>8 mm) were deleted. Animals with weaning ages between 120 and 300 days were included for the characteristic ww (limits established for the national genetic evaluation), and for W18, animals of 457 to 640 days of age were included (18 months ± 3 months). The edition was carried out using the statistical program sas9.
2.2 Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics of environmental effects were performed using the means procedure of the statistical program sas9. The effects of sex, herd, year of birth, management code, mother's age at parity, age at weaning, and age at 18 months were analyzed.
The study of the fixed effects on growth and carcass quality was carried out with the following model:
Regarding ww, the calf's age at weaning was included in the model as a covariate, and for w18, rea and rft the covariate age at 18 months. Possible interactions between effects were not considered due to the small number of records.
The analysis of fixed environmental effects included in the model was performed using the glm procedure of the statistical program sas9.
2.3 Connectedness
The study of connectedness between herds and years considered the same data as the analysis of environmental effects, and had information about the reference parents used.
The program conexf9010 was used to determine pevd and cr, considering weaning weight data grouped by year and cg, and assuming a heritability value of 0.30 for this characteristic according to the studies presented by Gregory and others11, and Phocas and Laloë12.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Environmental effects
The results of the descriptive statistics (Table 1) presented differences between males and females for all the characteristics, resulting in significant differences (p <0.05) for the characteristics, except for rft. The results of the model for growth and carcass quality are presented in Table 2.
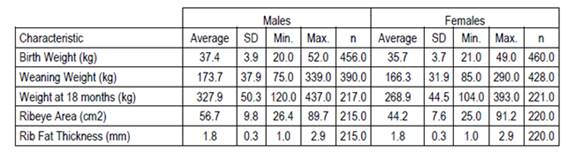
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of the sex effect for the characteristics: birth weight, weaning weight, weight at 18 months, ribeye area, and rib fat thickness.
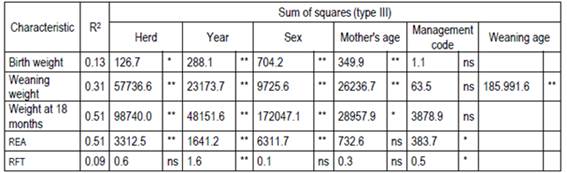
Table 2: Variance analysis for birth weight, weaning weight, weight at 18 months, ribeye area (rea), and rib fat thickness (rft) of Limousin animals.
The sex effect presented a significative value for the characteristics: wb, ww, w18 and rea, which coincides with the results of Simcic and others13, that worked with 167 Limousin animals, and Koch and Clark14, who with 5952 Hereford breed animals obtained that males were 1.2 kg and 11.8 kg heavier than females at birth and at weaning, respectively. Goldberg and Ravagnolo15, with Angus animals in Uruguay, found that the effects herd, year, and month of measurement of the characteristic were significant for the characteristics wb, ww, and w18. In this study with the Limousin breed, the herd and year effects significantly influenced all the characteristics, except for the herd effect for rft.
For their part, the Limousin calves born from 6 and 9-year-old mothers in this study were 1.9 kg (p<0.05) and 2.7 kg (p<0.01) heavier at birth than those from 2 to 4-year-olds, respectively. Meanwhile, 5, 7, and 8-year-old mothers had heavier calves at birth, but the differences were not significant with respect to 2 to 4-year-olds. Krupa and others16 reported similar results with various breeds, where 5 to 7-year-old mothers delivered the heaviest calves at birth. Koch and Clark14 obtained higher wb and ww in calves born to 3 to 6-year-old mothers. The inclusion in this work of a category of mothers where mothers with different ages were grouped because they did not have a date of birth could explain the differences with these authors.
The management effect was not significant to growth characteristics (wb, ww, and w18), which was striking given the differences in animal performance normally observed nationally when natural field, natural field and pasture, and only pasture managements are applied in the conditions of our country.
Weaning age covariate was significant for ww, where for each day animals presented 0.48 kg more at weaning (p <0.001), while covariate age at 18 months did not present statistical significance for w18, rea and rft.
3.2 Connectedness
From the information of the sires used by the herds and the effective offspring obtained in each herd, they were directly and/or indirectly connected only in the years 2013, 2014 and 2015. For 2012 there were only two herds, which were connected by a single parent. The number of sires used in common for the remaining years was three to four, with an average of six offspring per herd. In 2016, three herds were connected through two parents in common.
The average, minimum and maximum values of pevd of a herd with the others were 113.9, 27.8, and 354.3, respectively. Lower values of pevd would indicate a greater connectivity ranking between herds. pevd values from 2012 to 2016 tend to the reduction of these towards this last year (Table 3).
Table 3 shows pevd values and the connectedness rating (cr) between herds. The correlation between cr and pevd is -0.4517. The average, minimum and maximum values of cr of a herd with the other herds were 7.9, 0.03 and 58.6, respectively.
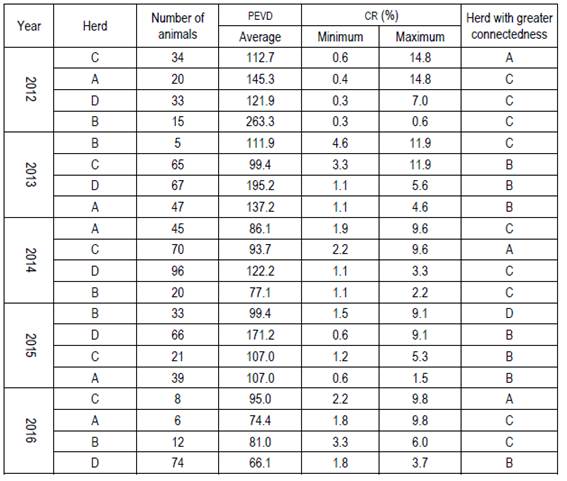
Table 3: Number of animals, minimum, maximum and herd which presents the highest connectivity ranking (cr), and prediction error variance average (pevd) per herd and year.
There are few references to cr values in the literature. Mathur and others8 worked with rear fat thickness in swines, and propose a connectivity ranking greater than 3%, as an acceptable cr value. Considering that value as a reference, the A, B, and C Limousin herds for 2016 have an acceptable degree of connectedness between them.
For their part, Roso and others17 studied different methods of measuring connectivity in bulls from a Canadian testing center They obtained an average value of pevd of 1726 between a group of animals and the rest, and a cr of 1.2%. Regarding the work carried out with the Limousin breed in Uruguay, the results are different for both measures, since average values of 113.9 and 7.9% were obtained for pevd and cr, respectively.
The results could be explained by the small size of the contemporary groups considered in the study since, as mentioned by Mathur and others8, it is recommended that the gc have at least ten animals and three different parents to obtain adequate connectedness values. Roso and others17 state that a group evaluated with few parents presents a greater variation in the pevd and cr, which indicates a greater variation in the degree of connectedness between groups. It is important to note that the smaller the number of animals per group, the pevd increases and the cr decreases.
Based on what was presented, the herds participating in the genetic evaluations of the Limousin breed for the evaluated years were directly and/or indirectly connected, but with low connectivity values (less than 3% of cr proposed by Mathur and others8) that did not yet warrant a population genetic evaluation.
4. Conclusions
The fixed environmental effects of year, sex, herd, age at weaning, and age at 18 months are relevant and should be included in studies associated with the genetic evaluation of the Limousin breed. In order to consolidate the population genetic evaluation of the breed in Uruguay, it is necessary to improve the connectedness rating between herds by using reference parents, and to present contemporary group sizes greater than or equal to 10 animals.















