Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Links relacionados
Compartilhar
Odontoestomatología
versão impressa ISSN 0797-0374versão On-line ISSN 1688-9339
Odontoestomatología vol.24 no.39 Montevideo jun. 2022 Epub 20-Abr-2022
https://doi.org/10.22592/ode2022n39e311
Update
MARPE-Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expander in young adults: Intermolar width, transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications, and other results. A systematic review
1Diplomado Ortopedia Temprana Facultad de Odontología, Universidad de Concepción.Chile
2Programa Atención Odontológica integral. Chile. mperezf@udec.cl
Objective:
To describe the results obtained with MARPE in young adults regarding intermolar width, the transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications, and other results.
Method:
We conducted a literature review following Prisma guidelines in Pubmed, SCIELO, Science Direct, Scopus, the System for Information on Grey Literature in Europe, Latin American and Caribbean literature in Health Sciences, and Google Academic. We also conducted a manual search of books and scientific papers. The full articles were analyzed, and nine articles were selected after applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results:
The literature indicates that MARPE increases transverse intermolar width and the transverse width of the nasal cavity. The periodontal and dentoalveolar complications reported are inconclusive.
Conclusion:
MARPE could be a clinically viable and effective treatment for young adults with transverse maxillary deficiency.
Keywords: maxillary expansion; young adults; palatal expansion technique
Objetivo:
Describir los resultados obtenidos con MARPE en pacientes adultos jóvenes en relación al ancho transversal intermolar, ancho transversal de cavidad nasal, complicaciones y otros resultados informados.
Método:
Se realizó un análisis siguiendo la guía Prisma, utilizando bases de datos Pubmed, SCIELO, Science Direct, Scopus, Sistema de información sobre literatura gris en Europa, Literatura Latinoamericana y del Caribe en Ciencias de la Salud, Google Académico, además de una búsqueda manual de libros y artículos científicos. Aplicando los criterios de inclusión y exclusión se analizaron 9 estudios.
Resultados:
MARPE aumenta el ancho transversal intermolar y el ancho de la cavidad nasal en pacientes adultos jóvenes. Las complicaciones periodontales y dentoalveolares registradas no son concluyentes.
Conclusión:
MARPE puede ser un tratamiento clínicamente viable y efectivo para pacientes adultos jóvenes que presenten deficiencia transversal maxilar.
Palabras clave: Expansión maxilar; adulto joven y técnica de expansión palatina
Objetivo:
Descrever os resultados obtidos com o MARPE em pacientes adultos jovens em relação à largura intermolares transversais, largura transversa da cavidade nasal, complicações e outros resultados relatados.
Método:
Foi realizada uma análise segundo o guia Prisma, nas bases de dados Pubmed, SCIELO, Science Direct, Scopus, Sistema de Informação sobre Literatura Cinza na Europa, Literatura Latino-americana e Caribenha em Ciências da Saúde, Google Acadêmico, além da busca manual de livros e artigos científicos. Aplicando os critérios de inclusão e exclusão, 9 estudos foram analisados.
Resultados:
MARPE aumenta a largura intermolar transversal e a largura da cavidade nasal em pacientes adultos jovens. As complicações periodontais e dentoalveolares registradas não são conclusivas.
Conclusão:
MARPE pode ser um tratamento clinicamente viável e eficaz para pacientes adultos jovens com deficiência transversa da maxila.
Palavras-chave: Expansão maxilar; adulto jovem e técnica de expansão palatina
Introduction and background
Transverse maxillary deficiency is one of the most frequent skeletal anomalies of the dental arches, regardless of the type of dentition. It can often be accompanied by posterior crossbite and dental crowding.1-2 It is a progressive condition that tends to increase in young people and may be permanent in adults.1 It has been reported that 9.4% of the population and about 30% of adult orthodontic patients have a transverse maxillary deficiency and a posterior crossbite.3-4
Multiple etiologic factors have been described for transverse maxillary deficiency. Some causes include developmental disorders such as cleft lip and palate, mouth breathing, and habits such as thumb sucking and atypical swallowing. Poor tongue posture, perioral muscle imbalance, and a lack of lip seal, along with labial hypotonicity, may also contribute to maxillary constriction.5
It is well documented that correcting transverse maxillary deficiency facilitates other orthodontic/orthopedic mechanics and improves facial and dental esthetics, oral function, nasal mucociliary clearance, and nasal breathing. Therefore, there has been ongoing research to improve treatment modalities for transverse maxillary deficiency and decrease the associated adverse side effects.5
Conventional rapid palatal expansion (RPE) has proven to be a reliable treatment method to correct transverse skeletal jaw disharmony in prepubertal patients.5 However, in adult patients, the technique has been considered impossible or rarely successful because the mid-palatal suture and adjacent joints begin to fuse and become stiffer in late adolescence.6 In particular, the bony palate and the zygomatic buttress show greater resistance to expansion.4,7 In adults, it has little or no skeletal effect.5 Detrimental dentoalveolar and periodontal effects have been described,2-4 such as thinning of the buccal alveolar bone plate,4 pain, tissue inflammation, unstable results, buccal tipping of crowns, gingival recession, root resorption, and ulcerations.6,8
Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion (SARPE) is a treatment of choice for transverse maxillary deficiency in young adults.3-4 However, due to the low adherence to complex surgical treatments and the increasing demand for non-surgical treatments,4,6,8 the miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expander (MARPE) is introduced.3,8 It is a miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion technique that can be used in young adults to open the midpalatal suture,4,8 correct transverse maxillary deficiency in adults,5 and maximize the orthopedic separation of the maxilla and overcome the disadvantages of tooth-borne and tooth-and-tissue-borne appliances.3,5
MARPE is a simple modification of RPE technique. Its main difference is the use of miniscrews4 anchored to the palate5 to ensure the expansion of the basal bone and maintain the separation between the bony structures during the consolidation period.4 Most MARPE appliances are tooth-bone-borne,2,4,6-7,9 although some are only bone-borne.1,3,5,8
Miniscrews can distribute the stress across the palate, decreasing the stress concentration around the abutment tooth.6 However, the information available regarding this novel technique’s skeletal, dentoalveolar, and periodontal effects is limited.5
To date, most studies have focused on the effectiveness of maxillary expansion in prepubertal patients.5
This review describes the results obtained with MARPE in young adults regarding intermolar width, the transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications, and other results.
Materials and methods
Search strategy. We conducted a literature review following Prisma guidelines in Pubmed (2010-2021), SCIELO (2010-2021), Science Direct (2010-2021), Scopus (2010-2021), the System for Information on Grey Literature in Europe, Latin American and Caribbean literature on Health Sciences, and Google Academic. We also conducted a manual search of books and scientific papers.
Search terms. The following keywords were used for the search: “maxillary expansion,” “young adult,” and “palatal expansion technique” related to the boolean operator AND. The DeCs terms used were “maxillary expansion,” “young adult,” and “palatal expansion technique.”
Inclusion/exclusion criteria. The following filters were applied: articles in English, Spanish, and Portuguese published from 2010 to 2021, case reports, clinical trials, cross-sectional studies, systematic reviews, editorials, and clinical guidelines available in full text. Posters, letters to the editor, expert comments, and partial texts were not considered. The last search was conducted on 24 April 2021. The articles included had to mention MARPE and include any of the variables evaluated: transverse intermolar width, the transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications, and other results. All of the above were evaluated in patients with transverse maxillary deficiency aged 18 to 25. The papers including the following exclusion criteria were not considered: patients with systemic disease, craniofacial syndrome, or dentofacial anomalies (cleft lip, cleft palate, or both). Studies where patients had undergone orthopedic, orthodontic, or surgical treatment before MARPE were also excluded.
Selection process The articles were selected independently by two reviewers. The titles were selected, and non-relevant publications were removed. The filters of each database were used by selecting the “search by date,” “search for clinical trials,” and “search for articles” options. The degree of reviewer Kappa concordance was 0.96 for article selection. The disagreements between the reviewers were solved with additional discussion.
Data collection. The following variables were searched for in each article:
Results
One hundred and seventy articles were classified within the search limits described above. Three additional papers were found in the manual search. Of these, 98 that were repeated were eliminated. After analyzing the titles and applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, nine studies were left for review, as shown in figure 1.
The data were extracted independently using tables 1 and 2 as data collection tools.
MARPE specifications per article are listed in Table 1. The data obtained from each piece for the variables transverse intermolar width, the transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications, and other results are specified in Table 2. We wrote “not mentioned” when the article did not include these variables, we wrote “not mentioned”.
Assessing risk of bias
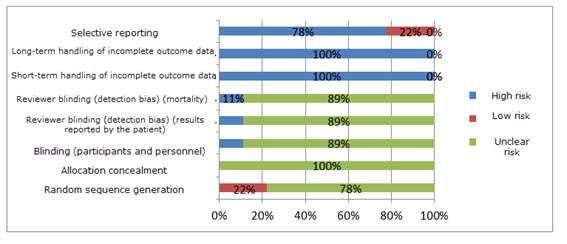
According to The Cochrane Collaboration guideline (2011), the risk of bias for the item “Random sequence generation” was “unclear” for 78% of the studies. (Figure 2).
The degree of bias was classified as “low risk” if all criteria were met, “moderate” if only one criterion was missing, and “high” if two or more criteria were missing.
Table 1: MARPE specifications
| Reference number | Mean age | Expander used | Miniscrews used | Activation protocol | Retention time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 | Rapid palatal expander. Bone-borne. | Four miniscrews: two 11 mm and two 9 mm long. Both are 2 mm in diameter. Spider Screw, Regular plus, HdC, Thiene, Italy. | Two activations a day until the midpalatal suture has opened and the maxillary constriction has been corrected. | 6 months |
| 2 | 20 | Conventional Hyrax expander with bands on first premolars and first molars. Two anterior hooks were placed on the rugae region, and the other two posterior hooks were placed on the parasagittal area. | Orthodontic miniscrews (Orlus, Ortholution, Seoul, Korea) with a 1.8-mm collar diameter and a 7-mm length. | The screw was turned once a day. The expansion was terminated at six weeks. | 3 months |
| 33 3 | Mean age 21.6 | Hyrax-type expander: (Hyrax II; Dentaurum, Ispringen, Germany) | Four miniscrews with a 1.8-mm collar diameter and a 7-mm length. (Orlus, Ortholution, Seoul, Korea). | The screw was turned once a day (0.2 mm) until the required expansion was achieved. The mean expansion was 6.54 (± 1.35) mm, and the expansion duration was five weeks. | 4 months |
| 4 | Mean age 18± 5.5 years | Hyrax-type expander. Bone-borne. | There are four miniscrews: two between canine and premolar and two between second premolar and first molar. The miniscrews are 10 mm long and 1.6 mm in diameter. (MOSAS self-drilling and self-tapping-Dewimed, Gac). | 2/4 turn in the morning and 2/4 turn in the evening. The time was calculated based on the expansion required for each patient. | 5 months |
| 5 | Mean age 20.9 ± 2.9 years | Hyrax type. Four stainless steel bars with hooks soldered at their base. | Four miniscrews that are 1.8 mm and 7 mm in diameter. Self-drilling. ORLUS, Ortholution, Seoul, Korea. | 1/4 turn (0.2 mm) every day. The expansion was terminated when the palatal cuspid of the permanent maxillary first molar came into contact with the tip of the corresponding buccal cuspid of the permanent mandibular first molar. | 3 months |
| 6 | Mean age 20.1 | Hyrax type. Four rigid bars with 0.8-mm stainless steel wire and hooks soldered to the base. (Hyrax® Click; Dentaurum, Ispringen, Germany). Two hooks were placed on the rugae area and the other two posterior hooks were placed on the parasagittal area. Cemented to the first premolars and molars. | Four orthodontic miniscrews with a 1.8 mm collar diameter and a 7-mm length (Orlus; Ortholution, Seoul, Korea). | One turn per day (0.2 mm) until the required expansion was achieved. | Not mentioned |
| 7 | Mean age 21.9 ± 1.5 years | Central expansion screw and four hooks soldered to orthodontic bands. Manufactured by BioMaterials Korea, Inc. It was placed in the anterior palate in four patients, and in four other patients, in the midpalate. Between two and four teeth were used for anchorage (mean=3.63). | Miniscrews 1.5 to 1.8 mm in diameter and 11 mm in diameter. | It varied according to the patient. The expansion was completed when the tip of the palatal cuspid of the maxillary first molars came into contact with the tip of the buccal cusp of the mandibular first molars. The average activation was 5.61 + 1.19 mm, with an average treatment time of 7.64 + 5.6 weeks. | Not mentioned |
| 8 | Group aged 20 to 29 | Expander (Peclab, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil). | Four orthodontic miniscrews (Peclab, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil) | 2/4 turn immediately after mini-implant placement and 2/4 turn daily, varying from 14 to 18 days until transverse correction was achieved. | 4 months |
| 9 | Mean age 20.4 ± 3.2 years | Central expansion screw placed in the posterior palate | Four 1.5 x 11 mm miniscrews | Two activations a day (0.40 mm) until a diastema appeared. Then, the activation changed to once a day. The expansion was complete when the maxillary basal bone was greater than the mandibular width. The average duration of expansion was 35 ± 10 days. | 6 months |
Table 2: Addressing each variable: Transverse intermolar width, transverse width of the nasal cavity, complications and other results
| Reference number | Title of study | Variables evaluated after implementing MARPE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transverse intermolar width | Transverse width of the nasal cavity | Complications | Other results | ||
| 1 | Class III malocclusion and bilateral crossbite in an adult patient treated with miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expander and aligners. | Increased | Not mentioned | Thickness of the buccal alveolar bone plate of the first permanent molar (M1): Decreased | Orthopedic expansion: Achieved. Gingival recession: Did not increase. Dental tipping: well controlled. |
| 2 | Miniscrew-assisted non-surgical palatal expansion before orthognathic surgery for a patient with severe mandibular prognathism. | Increased | Increased | Transitional soft-tissue inflammation. | Transverse intercanine width: Increased Separation of midpalatal suture: confirmed. Periodontal tissue: No significant changes |
| 3 | Stability of dental, alveolar, and skeletal changes after miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion | Increased | Increased | Inclination of M1: Moved buccally. Inclination of alveolar bone: Moved buccally. Buccal alveolar bone thickness of PM1: Decreased. Buccal alveolar bone thickness of PM1: Decreased. Buccal alveolar crest level of PM1: Towards apical. Buccal alveolar crest of PM1: Moved apically. | Increased: Intercusp width of central incisors Intercusp width of canines Intercusp width of PM1 Intercusp width of PM2 Interapex width of incisors Interapex width of canines Interapex width of PM1 Interapex width of PM2 Palatal alveolar bone thickness of PM1 Palatal alveolar bone thickness of PM2 Palatal alveolar bone thickness of M1 Statistically not significant: Buccal alveolar bone thickness of PM2 |
| 4 | Rapid maxillary expansion in young adults: comparison of tooth-borne and bone-borne appliances, a cohort study. | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Statistically not significant: Inclination of right PM1 Inclination of left PM1 Inclination of right upper incisor Inclination of left upper incisor Anterior transverse dimension (ATD) Increased: Posterior transverse dimension (PTD) Radiolucency of the midpalatal suture: In 100% of patients. |
| 5 | Non-surgical miniscrew-assisted rapid maxillary expansion results in acceptable stability in young adults | Increased | Increased | Not mentioned | Midpalatal suture opened in a Triangular shape. Opening of midpalatal suture: 86% of participants. Increased: Intercanine width Interpremolar width Statistically not significant: Clinical crown height: |
| 6 | Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes after miniscrewassisted rapid palatal expansion in young adults: A cone-beam computed tomography study | Increased | Increased | Buccal bone thickness of PM1: Decreased. Buccal bone thickness of M1: Decreased. Buccal alveolar height of PM1: Decreased. Buccal alveolar height of M1: Decreased. Buccal inclination of maxillary M1: Increased | Zygomatic arch width: Increased. Expansion pattern (coronal plane): pyramidal. Expansion pattern (sagittal plane): parallel. Opening of midpalatal suture: 84.2% of participants. Skeletal, alveolar, and dental expansion: 37.0%, 22.2%, and 40.7%, respectively. |
| 7 | Retrospective Evaluation of Skeletal, Dentoalveolar, and Periodontal Changes of Microimplant Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) In Skeletally Matured Patients | Increased | The expansion of the nasal cavity areas is equivalent to 45% of the expansion achieved with MARPE. | Buccal alveolar bone thickness of PM1: Decreased. Buccal alveolar bone thickness of M1: Decreased. Dental inclination of left PM1: towards vestibular. Dental inclination of right M1: moved buccally. Dental inclination of left M1: moved buccally. | Opening of midpalatal suture: in 100% of cases and without removing microimplants. Expansion: 41% skeletal, 12% alveolar bone, and 48% tooth tipping. Expansion pattern: parallel in coronal and axial planes. Right zygomatic area: it expanded. Left zygomatic area: it expanded. Right infrazygomatic area: it expanded. Left infrazygomatic area: it expanded. |
| 8 | Evaluation of factors related to the success of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Increased: Anterior palate transverse dimension Posterior palate transverse dimension Midface width (measurement between infraorbital foramens) |
| 9 | An assessment of the magnitude, parallelism, and asymmetry of microimplant- assisted rapid maxillary expansion in non-growing patients | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Post-expansion transverse asymmetry: 51% of patients | Increased: Transverse dimension at the anterior nasal spine. Transverse dimension at the posterior nasal spine. |
Transverse width of the nasal cavity
This variable increases in all the articles reviewed. The transverse width of the nasal cavity increases 1.07 mm immediately after MARPE removal6 to 2.2 mm, a value recorded 10 months post-treatment.4
Expansion of the nasal cavity resulted in increased airflow and improved nasal breathing.8
Complications
Studies report periodontal and dentoalveolar complications, including:
1. Thinning of the buccal bone plate: Thinning of the buccal bone plate of the first molar.3,7 In any case, the teeth still had adequate bone coverage in the roots.3 The same result is reported for the first molar and the first premolar.5,7-8
2. Inflammation: Transitional soft-tissue inflammation surrounding the miniscrews in the palate was recorded during MARPE treatment. This decreased when the device was removed once the budgeted time for expansion had elapsed. There is no indication of treatment interruption.4
3. Apical shift of alveolar ridge: An apical shift of the ridge is reported in the first molar and the first premolar.7-8
4. Tooth angulation: There is a change in the tip of the first molar after MARPE treatment.5,7-8). It moved buccally by 3.91°.7
The angulation of the left first premolar moved buccally. The angulation change of the contralateral tooth was not statistically significant.5
5. Movement of alveolar bone: Significant results are recorded for the alveolar bone of the first molar. It varies 1.78° buccally.7 This contrasts with another study showing statistically significant results for first premolars and first molars.5
6. Transverse asymmetry post-MARPE: 51% of patients had asymmetry of at least 1.1 mm in the expansion of the anterior nasal spine.2
Other results: The literature records other variables.
1. Skeletal expansion: Orthopedic expansion is described, even correcting a bilateral crossbite.3
2. Periodontal tissue: studies do not indicate gingival recession (3-4;7) immediately after MARPE treatment, nor significant changes in dental crown height4,6 or bone dehiscence. Periodontal support remained solid and stable.4
3. Opening of palatal suture: All studies show opening, achieving an 84.2% (8) and higher success rate.1,5-6
4. Opening pattern: It is pyramidal in the coronal plane,6,8 with the smallest increase in the nasal cavity and the most significant increase in intermolar width.6 Another author indicates a parallel expansion pattern.5 The expansion follows a parallel pattern in the axial plane.5,8
5. Transverse measurements: The previous transverse dimension values were not statistically significant.1 However, Oliveira et al.9 report a significant increase. Intercanine width3-4;6 and interapex width of incisors and canines also increases.4
6. The posterior transverse dimension increases,1,9 along with the intercuspid width of first premolars and second premolars4,6 and the interapex width of first premolars and second premolars.4
7. After MARPE treatment, the studies recorded an increase in the width of the zygomatic arch,8 zygomatic area,5 infra-zygomatic area,5 and the region between the infraorbital foramens.9
Discussion
Chronological age is a good predictor of MARPE success (disjunction), showing a negative Pearson correlation. This means that the older the patient, the lower the chances of MARPE success and the less opening and skeletal expansion.9 However, age should not be the only factor to consider.9)
The literature is contradictory: the data show intrasutural and interindividual variability in the developmental stages of the midpalatal suture, which is not directly related to chronological age.5 Midpalatal suture fusion varies with gender and age. Fusion of the midpalatal suture has been reported in patients aged 15 to 19, and lack of fusion has been reported in patients aged 32, 54, and 71.5 This would explain the different MARPE success rates and the variable increases post-MARPE. The most significant increase in transverse intermolar width immediately after MARPE removal is 8.32 mm,6 followed by 8.3 mm,4 and 6.26 mm.5 The greatest increase in transverse width of the nasal cavity recorded is 2.2 mm.4,7
The decision to use appliances such as MARPE or tooth-borne devices in young adult patients should be based on patient characteristics: skeletal maturity, palate shape, hygiene, teeth present, condition of dental crowns, and orthodontist’s preferences.1,5 Therefore, anchoring MARPE to the palate with miniscrews4 can be very useful in patients who have missing or compromised posterior teeth.1
Miniscrews allow clinicians to perform orthodontic therapy and expansion simultaneously, which reduces treatment times.1 In addition, skeletally-anchored expanders produce more significant orthopedic expansion than tooth-borne devices.1,6 Both show an increase in the anterior transverse dimension. However, on average, this is greater in patients treated with 2.4 mm versus Hyrax 1.9 mm miniscrews.1
Four of the nine articles reviewed use bone-borne MARPE devices.1,3,5,8 The rest of the MARPE devices are bone-tooth-borne. It would be interesting to compare the results obtained with these two devices in young adults.
Only one study2 refers to the symmetry of the resulting expansion. Considering the records obtained, it would be useful to conduct further studies on the expansion of the anterior nasal spine.2
No study has recorded clinically significant gingival recession immediately after MARPE use. However, in the future, this should be monitored, given the changes in the alveolar bone, apical migration of the alveolar ridge, and inflammation.7-8
Only one study mentions the millimeters of transverse discrepancy for which MARPE is effective. MARPE corrects mild to moderate maxillary transverse discrepancies of less than 7 mm in skeletally mature patients with a healthy periodontium.5
Regarding maintaining the results obtained with MARPE, a post-treatment relapse of 0.07 mm in the intermaxillary width was recorded.9 More long-term studies are needed to evaluate this item.
One of the potentia limitations of this review is that we included studies with patients of different races, skeletal maturity, and craniofacial anatomy. The number of microimplants varied, and there was a lack of long-term follow-up because MARPE was continued with orthodontic or surgical treatment. The degree of activation and containment of each device was different for each patient. The lowest activation frequency was one turn per day and the highest was two turns per day. The longest activation time reported was seven weeks.5 This study reports that the expansion of the nasal cavity areas is equal to 45% of the expansion achieved with MARPE.5
Conclusion
The studies reviewed indicate that MARPE could be a clinically viable and effective treatment for young adults with transverse maxillary deficiency. After separation of the palatal suture, intermolar transverse width and the transverse width of the nasal cavity increase.
Periodontal and dentoalveolar complications reported in the literature are mild in magnitude and inconclusive. Among them, the most common are thinning of the buccal plate of the alveolar bone of the first molar and first premolar, and tipping of the first molar.
Recent literature suggests that chronological age should not be the only factor to consider in evaluating the prognosis of this treatment.
Randomized clinical trials involving more patients and long-term follow-up are required to assess the success of MARPE and the stability of post-treatment expansion.
REFERENCES
1. Rojas V, Macherone C, Zursiedel MI, Valenzuela JG. Rapid maxilary expansion in young adults: comparison of tooth-borne and bone-borne appliances, a cohort study. J Oral Res 2019; 8 (3): 201-209. [ Links ]
2. Elkenawy I, Fijany L, Colak O, Paredes NA, Gargoum A, Abedini S, Cantarella D, Dominguez-Mompell R, Sfogliano L, Moon W. An assessment of the magnitude, parallelism, and asymmetry of micro-implant-assisted rapid maxillary expansion in non-growing patients. Prog Orthod. 2020; 21(1):42. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7680816/ [ Links ]
3. Lombardo L, Carlucci A, Maino BG, Colonna A, Paoletto E, Siciliani G. Class III malocclusion and bilateral cross-bite in an adult patient treated with miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expander and aligners. Angle Orthod. 2018; 88(5): 649-664. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29714067/ [ Links ]
4. Lee KJ, Park YC, Park JY, Hwang WS. Miniscrew-assisted nonsurgical palatal expansion before orthognathic surgery for a patient with severe mandibular prognathism. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010; 137(6): 830-9. [ Links ]
5. Nguyen UK. Retrospective Evaluation of Skeletal, Dentoalveolar, and Periodontal Changes of Microimplant Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) In Skeletally Matured Patients 2017 (Tesis). West Virginia University. Disponible en: https://researchrepository.wvu.edu/etd/6310 [ Links ]
6. Choi SH, Shi KK, Cha JY, Park YC, Lee KJ. Nonsurgical miniscrew-assisted rapid maxillary expansion results in acceptable stability in young adults. Angle Orthod. 2016; 86(5): 713-20. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26938955/ [ Links ]
7. Lim HM, Park YC, Lee KJ, Kim KH, Choi YJ. Stability of dental, alveolar, and skeletal changes after miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion. Korean J Orthod. 2017; 47(5): 313-322. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28861393/ [ Links ]
8. Park JJ, Park YC, Lee KJ, Cha JY, Tahk JH, Choi YJ. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes after miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion in young adults: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Korean J Orthod. 2017; 47(2): 77-86. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28337417/ [ Links ]
9. Oliveira CB, Ayub P, Angelieri F, Murata WH, Suzuki SS, Ravelli DB, Santos-Pinto A. Evaluation of factors related to the success of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansión Angle Orthod 2021; 91(2):187-194. Disponible en: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33351888/ [ Links ]
Conflict of interest declaration: The authors have no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Authorship contribution: 1. Conception and design of study 2. Acquisition of data 3. Data analysis 4. Discussion of results 5. Drafting of the manuscript 6. Approval of the final version of the manuscript APF has contributed in: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. JSS has contributed in: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
Received: August 17, 2021; Accepted: September 17, 2021











 texto em
texto em