1. Introduction
Protected or under-cover crops are a very important form of production within Uruguay's horticulture, particularly in the northern area. This zone, which accounts for 21% of the total area dedicated to horticulture, contributes 39% of national horticultural production and concentrates 81% of total protected production1. The most common protected crops in this area are, tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), and pepper (Capsicum annuum), produced in winter and spring ("early crops" or "off-season crops") to supply the domestic market, especially in Montevideo. The main destination of tomato cultivation is fresh consumption (table tomato). In 2009, the off-season tomato production reached 21.6 thousand tons, accounting for 68% of the total national supply for fresh consumption1).
Within the northern horticultural area, located in the departments of Artigas, Salto, and Paysandú, the production near the city of Salto is of great importance, developed mainly on "Argisoles Dístricos Ócricos" soils of the Salto Unit. These soils are loamy-sand and sandy-loam, with moderate to good drainage and, in their natural state, slightly acidic (pH 5.5), of very low natural fertility, with low organic matter content (10-20 g kg-1) and cationic exchange capacity at pH 7 (CICpH7) lower than 10 cmol kg-1)2)(3.
It is common in these horticultural production systems to carry out repeated tillage to prepare the planting bed and fight weeds4. In addition, organic amendments are usually added to improve some physical soil properties, such as water infiltration and retention, macroporosity, etc.5)(6, and also as a pest control strategy (biofumigation)7)(8)(9. Another common technique is to cover the soil with plastic to induce hydrothermal processes to control pests and weeds (solarization)10)(11.
Numerous studies have shown that the over-application of organic and inorganic amendments together with frequent tillage can lead to changes in nutrient dynamics, acidification, and/or accumulation of salts in the soil, which compromise the sustainability of the production system and the environment. High N inputs can cause nitrate leaching losses (NO3 -) in depth, denitrification and volatilization of ammonium (NH4+)12, in addition to an increase in crop susceptibility to some diseases13. Also, the application of ammoniacal sources of N in high doses, as well as highly extractive continuous crops or organic matter loss in the soil can decrease cation content and cause acidification, even in no-tillage systems, as demonstrated by a recent study in agricultural soils in Uruguay14. The accumulation of P in the surface layer of the soil may increase the risk of losses from surface runoff and even by leaching or preferential flow15. Salts that accumulate in the soil rooting zone come from the supply of salt-rich irrigation water, organic amendments, fertilizers, or other chemicals, or natural mechanisms such as the mineralization of soil organic matter, the upward movement of ions with evapotranspiration water, or selective absorption by crops16)(17. This accumulation of salts can negatively affect crop yield or increase soil pH and change the distribution of interchangeable cations6. Salt levels corresponding to electrical conductivity (ec) of between 4 and 8 dS m-1 (measured in saturated paste extract) affect most crops' growth, although there are moderately sensitive crops which developments are affected by ec values between 2 and 4 dS m-1, such as tomato and pepper18)(19. Increasing pH in the soil may decrease the availability of micronutrients (Fe, Zn, and Mn), and induce deficiencies in plants6)(20. In soils with horticultural production under plastic cover in Uruguay, the high observed pH values (between 6.5 and 7.5) in light-textured soils in the northern area were attributed to the continued use of waters rich in calcium bicarbonate21. According to an irrigation water characterization study in Uruguay, well water used for irrigation in the northern area presents low salt concentration (ec lower than 1 dS m-1), a low risk of sodicity problems, and predominance of Ca bicarbonate (conversation with J. Zamalvide; unreferenced).
Although the northern horticultural area and, therefore, tomato as its main crop are of great relevance to the country, information on the current state of soils in that area with horticultural crops in greenhouse is scarce21. Given the natural characteristics of these soils, together with common management practices (frequent tillage, high doses of organic and inorganic nutrient sources and irrigation), some properties may have been affected, negatively affecting crop production or presenting a potential environmental risk. Therefore, the objective of this study was to characterize soils under greenhouses in the northern part of the country, by analyzing some physicochemical properties and linking them with typical management practices of those production systems. For this, greenhouses in horticultural farms near the city of Salto were selected.
2. Material and methods
2.1 Selection of farms and greenhouses
From the horticultural area located around the city of Salto, 30 commercial farms were selected, with tomato under greenhouse as their core business. The sample, 23622 farms, constitutes almost 13% of the total number of farms dedicated to protected tomato crops in the north and covers representative situations in terms of production and general crop management. Figure 1 shows the location of the selected farms.
2.2 Information on management practices
A survey was conducted with the people in charge of each farm, completing a form with pre-established questions, to know general aspects such as: total area; protected crop area (greenhouses, macrotunnels and microtunnels), and field crop area (uncovered). In addition, information on crop management was collected regarding: yield obtained in the year of study, used varieties, number of consecutive tomato crops in the greenhouse, organic amendments, and applied fertilizers (dose, and form and time of application).
Based on the information provided on amendments and bibliography values, the nutrient supply was estimated. The number of consecutive tomato crops in the same greenhouse was taken as an indicator of the management history, assuming that the same practices were carried out for soil work, application of organic amendments, fertilization and irrigation.
In all the studied farms, the greenhouses had fixed wooden structures covered with transparent plastic. After harvesting each crop, tillage was carried out with chisel plow and cultivator, and roto-tiller or disk-plow were used to make the furrows (approximately 0.20 m high, 0.80 m wide and a variable length between 80 and 100 m).
2.3 Soil sampling
The most representative greenhouse of each farm was selected as indicated by the interviewee, seeking heterogeneity in the history of horticultural use. From the selected greenhouse process, soil samples were taken in 2011 during the November-December period, which coincides with the completion of the production cycle of tomato cultivation in the study area. Soil composite samples (at least 12) were taken with a borer randomly, at two depths (0 to 20 and 20 to 40 cm), avoiding the edges of the furrows. Before their physicochemical characterization, the samples were dried during 48 h at 40 °C, sieved, and then ground to less than 2 mm. osc (g kg-1), pH, interchangeable cations (cmol kg-1), cation exchange capacity at pH 7.0 (CECpH7, cmol kg-1), EC (dS m-1), available P (mg kg-1) and texture were determined in samples from 0 to 20 cm; pH was determined in water and in KCl by potentiometry (using a soil:solution ratio of 1:2.5 v:v). osc was obtained by combustion at 900 °C using LECO TruSpec23 equipment. The interchangeable cations (Ca, Mg, K and Na) were extracted with Ammonium Acetate 1 M at pH 7.024, and determined by atomic absorption (Ca and Mg) and atomic emission (K and Na). The ec was measured by conductimetry (using a soil:solution ratio of 1:1 v:v) (Dahnke and Whitney method25). cec pH7 was determined following the procedure by Camargo and others26. The extractable P was obtained by the Bray 1 method27 and determined by colorimetry according to Murphy and Riley28. The Bouyucus method was used to determine texture29. Ammonium was measured in all samples (NH4 +) (mg kg-1) by the colorimetric method30, and nitrate (NO3 -) (mg kg-1) by potentiometry, according to Gelderman and Beegle31. All chemical and physical analyses were carried out at the Soil Laboratory of the Alberto Boerger Experimental Station, inia, La Estanzuela (Colonia, Uruguay).
2.4 Data analysis
Descriptive statistics summarized the information provided by the interviewees and the data from the physicochemical determinations of soil samples. The relationships between the measured variables and the data provided were studied using Pearson correlation coefficients (r) and multiple linear regression. A value of P equal to 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1 General characteristics of farms and management practices
The total area of the surveyed farms ranged from 2 to 39 ha, although the majority (80%) had an area smaller than 15 ha (Figure 2A). In addition, the average greenhouse area was 1.5 ha or smaller, in 83% of the cases (Figure 2B).
Out of the 30 farms, 19 had field crops, apart from the greenhouse production, and eight had crops under macro and micro-tunnels (Table 1).
Organic amendments, mineral or inorganic fertilizers, and irrigation are applied on all selected farms as usual practices. The most frequently applied amendment (60%) is a mixture of cattle manure with remnants of soil (mulch) and shelter trees, followed by cattle manure (poultry manure) (37%) and waste of other crops (such as pepper or sorghum (Sorghum spp.)) (20%). The average dose of mulch is 50 Mg ha-1, but it varies between 20 and 82 Mg ha-1 of dry matter. According to interviewees, amendments are applied into the soil during January and February for biofumigation, or a few days prior to transplantation in March. In the greenhouses studied, solarization is also carried out (Table 1).
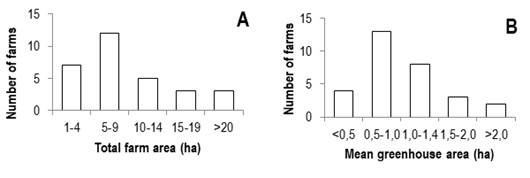
Figure 2: Number of farms according to total area (A) and number of farms according to average area per greenhouse (B)
Table 1: Information on surface distribution, tomato variety, organic amendments and fertilizers applied to the studied farms.
| Number of farms | Additional information † | |
| Area (ha) | ||
| Total | 30 | 10 (2 - 39) |
| Greenhouses | 30 | 1.03 (0.12 - 3.00) |
| Macrotunnels | 1 | 1 |
| Microtunnels | 7 | 0.63 (0.20 - 1.05) |
| Field crops | 19 | 2.50 (0.25 - 10.00) |
| Variety of tomato | 30 | Elpida |
| Organic amendments | 27 | Way and time of application: incorporated to the soil, before transplantation. |
| 18 | Mulch. Dose: 50 (20-82) Mg ha-1 of dry matter | |
| 11 | Poultry manure. Dose: (10 (7 - 12) Mg ha-1)). | |
| 6 | Pepper and sorghum remains. | |
| Biofumigation | 30 | |
| Solarization | 30 | |
| Irrigation by dripping | 30 | |
| Fertilization | 30 | Dose of N, P and K (kg ha-1): 90.84 and 201 kg and Mg (80-100 kg ha-1 of MgO). Way and time of application: incorporated to the soil, before transplantation. During growth: Foliar Ca |
† Average values and between parenthesis, minimum and maximum.
On all premises, water is applied by drip irrigation system, in a total volume of approximately 400 mm, distributed according to crop demand (Table 1).
Of the total N and K applied as fertilizers, approximately 23% of N and 30% of K are applied to the soil before transplantation. The rest of these nutrients are applied during the crop cycle through irrigation water. Almost all P is incorporated into the crop transplant (Table 1). According to the interviewees, inorganic fertilizer doses are recommended in the area and are based on the amounts a tomato crop would require to produce 150 Mg ha-1. None of the farms regularly analyzes soils, irrigation water or amendments.
3.2 General characteristics of sample greenhouses
On all grounds, the tomato variety used was Elpida; but the yield information obtained in the 2011 harvest in the sample greenhouses was provided on 20 of the 30 premises, as the rest had no records. The average crop yield in the selected greenhouses was 131 Mg ha-1, although it ranged from 90 to 190 Mg ha-1 (Table 2). Except for Mg, no relationships were observed between yield and the rest of the variables studied (Table 3). The number of consecutive tomato crops in the selected greenhouses was negatively related to the total area of the site (Table 3).
Table 2: Statistical summary of farm areas, greenhouses, number of consecutive tomato crops, yield and chemical properties of soils in the studied greenhouses.
| Mean | SD | Maximum | Minimum | Median | 25% | 75% | |
| Total farm area (ha) | 10.4 | 8.5 | 39 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 13.5 |
| Greenhouse area (ha) | 1.0 | 0.7 | 3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1.2 |
| No. consecutive crops | 9 | 5 | 18 | 2 | 9 | 5 | 14 |
| Yield, Mg ha-1 | 131 | 31 | 190 | 90 | 120 | 100 | 150 |
| Mulch, Mg DM ha-1 | 50 | 15 | 82 | 20 | 49 | 41 | 60 |
| SOC, g kg-1 | 14.34 | 4.1 | 23.5 | 7.8 | 13.7 | 11.4 | 18.5 |
| pH water | 7.3 | 0.6 | 8.4 | 6.1 | 7.4 | 6.8 | 7.9 |
| pH KCl | 6.57 | 0.572 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 6.7 | 6.1 | 7.1 |
| Ca, cmol kg-1 | 8.04 | 2.98 | 15.7 | 3.6 | 7.4 | 5.8 | 9.2 |
| Mg, cmol kg-1 | 1.69 | 0.61 | 3.1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 2.3 |
| K, cmol kg-1 | 0.409 | 0.257 | 1.15 | 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.48 |
| Na, cmol kg-1 | 0.624 | 0.372 | 2.24 | 0.2 | 0.545 | 0.43 | 0.69 |
| CEC pH7, cmol kg-1 | 11.443 | 3.70 | 20.4 | 5.6 | 10.75 | 8.4 | 12.7 |
| NO3 - (0-20), mg kg-1 | 36 | 37 | 161 | 6 | 20 | 12 | 50 |
| NH4 + (0-20), mg kg-1 | 12 | 12 | 44 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 13 |
| Mineral N (0-20), mg kg-1 | 48 | 38 | 168 | 9 | 36 | 22 | 63 |
| NO3 - (20-40), mg kg-1 | 19 | 30 | 166 | 3 | 12 | 7 | 17 |
| NH4 + (20-40), mg kg-1 | 16 | 22 | 108 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 16 |
| Mineral N (20-40), mg kg-1 | 34 | 35 | 171 | 6 | 22 | 14 | 40 |
| EC, dS m-1 | 1.25 | 0.63 | 2.93 | 0.52 | 1.04 | 0.81 | 1.46 |
| P Bray 1, mg kg-1 | 74 | 25 | 137 | 2 | 78 | 65 | 89 |
| Sand, % | 82 | 9 | 96 | 59 | 84 | 76 | 88 |
| Silt, % | 9.2 | 4 | 20 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 12 |
| Clay, % | 8.7 | 5 | 20 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 10 |
† n= 20; ‡ n= 183.3 Physicochemical soil properties
The dominant texture in the first 20 cm of depth varied between loamy-sand and sandy-loam, with similar sand, silt and clay values between farms (Table 2). These values correspond to fractions after sieving for the separation of the thickest fraction (gravel).
In general, the soils presented high values of soc, pH, P, and very low values of K.
The soc levels in the studied soils correspond to values between 11 and 32 g kg-1 of som (Table 2). The soc was positively related to Ca, Mg and K and also to the level of NO3 - at the two sampling depths (Table 3). Based on multiple linear regression analysis, soc increased when increasing the total area of the farm and interchangeable Ca content (Table 4).
Table 3: Pearson correlation coefficients (r) between total farm and greenhouse area, number of consecutive tomato crops, yield obtained in the studied cycle, amount of applied amendment, and chemical properties of the soil.
| No. Crops | Yield | SOC | Water pH | Ca | Mg | K | Na | NO3 - (0-20) | NH4 + (0-20) | NO3 - (20-40) | NH4 + (20-40) | EC | P Bray 1 | |
| Area Total | -0.37 | -0.38 | -0.32 | -0.34 | -0.31 | |||||||||
| Area Greenhouse | 0.41 | -0.31 | ||||||||||||
| No. crops | 0,47 | 0.35 | 0.31 | |||||||||||
| Yield | 0.43 | -0.41 | 0.49 | |||||||||||
| SOC | -0.33 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.35 | |||||||
| Water pH | -0.4 | |||||||||||||
| Ca | 0.85 | 0.32 | -0.31 | 0.35 | ||||||||||
| Mg | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.39 | |||||||||||
| K | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.32 | ||||||||||
| Na | 0.46 | |||||||||||||
| NO3 - (0-20) | 0.80 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||
| NH4 + (0-20) | 0.85 | |||||||||||||
| NO3 - (20-40) | 0.51 |
† Area. Total: Total farm area; ‡ Area. Greenhouse: Greenhouse area
The pH was positively related to the number of consecutive tomato crops, and negatively to both farm area and level of NO3 - (Table 3). According to the multiple linear regression analysis, the pH increased with the number of consecutive tomato crops in the greenhouse and decreased with the level of NO3 - at 20 cm deep (Table 4).
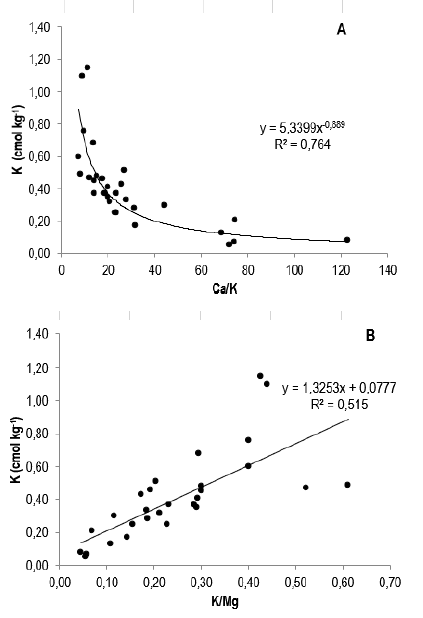
Regarding K, although the mean and median were similar, values as low as 0.05 cmol kg-1 and as high as 1.15 cmol kg-1 (Table 2) were observed. Ca and Mg, and Mg and K contents were positively related to each other (Table 3). The Ca:Mg cationic ratio was lower than 10 in most soils, but ratios of Ca:K greater than 30 (Figure 3A) and K:Mg lower than 0.15 (Figure 3B) were observed. The interchangeable Na values were less than 0.69 cmol kg-1 (which was the 75th percentile), although a value of 2.24 cmol kg-1 was observed (Table 2).
The average extractable P measured by the Bray 1 method presented a mean of 74 mg kg-1, with values concentrated between 66 and 89 mg kg-1 (25th and 75th percentile, respectively), although it ranged from 2 to 137 mg kg-1 (Table 2). No significant relationship was found to P=0.05 between the extractable P level with any of the variables analyzed, including the quantities of mulch or the number of consecutive crops in the greenhouse (Table 3).
The dominant fraction of mineral N was NO3 -, versus NH4 +, although both fractions were highly variable in the two depths (Table 2).
The level of NO3 - in the upper soil layer was positively related to soc, Mg, K and ec, but negatively to pH (Table 3).
The concentration of NO3 - at 20-40 cm deep was also positively related to the soc, K, ec, and with the level of NO3 - of the upper layer (Table 3).
In most of the analyzed soils, the ec values were less than 2.0 dS m-1, but soils with values close to 3 dS m-1 (Table 2) were also recorded. A linear and positive relationship was observed between ec and the cations K and Na, and also with levels of NO3 - in both depths (Table 3). According to the multiple linear regression analysis, the ec increased with the increase of Na and NO3 - (Table 4).
Table 4: Multiple linear regression coefficients between soil organic carbon (SOC), pH and electrical conductivity (EC), and properties of the soil or the productive system
| Variable | Coefficient | P Value | |
| SOC | Constant | 0.389 | 0.049 |
| Total farm area | 0.016 | 0.02 | |
| Ca | 0.109 | <0.001 | |
| pH | Coefficient | P | |
| Constant | 6.981 | <0.001 | |
| No. consecutive crops | 0.0691 | <0.001 | |
| NO3 - (0-20) | -0.00845 | 0.001 | |
| EC | |||
| Constant | 0.52 | 0.002 | |
| Na | 0.516 | 0.016 | |
| NO3 - (0-20) | 0.011 | <0.001 |
4. Discussion
The chosen variety was the same in all farms and has important characteristics, such as precocity and high yield, among others32. In the pre-sampling cycle, the average yield of greenhouses with records was below the average reported in that harvest for the north (150 Mg ha-1)1.
The soils under study are representative of the modal soils described for the area2.
The high values observed for current soc are attributed to residual effects of the application of high doses of organic amendments. In a study carried out on horticultural soils in southern Uruguay, García de Souza and others33 found that after six years of annual amendment application to soils with 28.2 Mg ha-1 of soc, an increase of 1.2 Mg ha-1 of cos was achieved (4% compared to the initial value). These authors applied annually 6 Mg ha-1 of dry matter of "poultry bed" (poultry manure mixed with rice husk, 266 g kg-1 of C) and 5 Mg ha-1 of dry matter from crop remains (such as Oatmeal sativa, Triticum aestivum, Setaria itálica, among others, with an average of 387 g kg-1 of C). In this study, 2.9 Mg ha-1 C are estimated to become part of the soc, with the average dose of mulch, assuming a C concentration of 176 g kg-1(34, an assimilation ratio of 1:3 and a C:N ratio of soil microorganisms of 10:134, in addition to considering losses by natural mineralization (3% per year). The effect of mulch aggregate could be considered to have less impact on the soc due to its C:N ratio (16 according to Barbazán and others35). Organic remains with C:N ratio lower than 20 are expected to have less effect on increasing soc than those with higher ratios36)(37)(38. On the other hand, a higher rate of mineralization of organic remains applied to the soil is expected in soils with lower clay content, such as those in this study, due to greater accessibility of microorganisms and less protection of organic material by clays39). The minor effects on the soc attributable to this type of amendment in these soils could be compensated by the high doses applied annually (50 Mg ha-1 dry matter, Table 2). Other possible contributions of C in the studied farms, such as crop remains after the end of the production cycle, were not considered in this analysis due to inaccuracy in the reported quantities.
The positive relationship observed between soc and farm size and between soc and Ca, Mg and K cations could be attributed to the frequency of soil use (higher in smaller land). A higher frequency of soil use would involve a greater amount of tillage that would induce an increase in the mineralization of som and erosion losses, according to Rabuffetti6, in addition to greater extraction of these nutrients by the crops.
Regarding pH, values higher than 7.0 were also observed by Moltini and Zamalvide21) in soils and production systems similar to those of our study. The increase in pH with the number of consecutive tomato crops in the same greenhouse partially supports the suggestions of Moltini and Zamalvide21 that the continued use of irrigation water rich in Ca bicarbonates (northern irrigation water characteristics, according to these authors) could have increased soil pH, although water was not analyzed in our study. As mentioned above, the number of consecutive tomato crops in the same greenhouse was taken as an indicator of the history of normal practices in the greenhouse (such as the application of organic amendments, inorganic fertilizers and irrigation). Consequently, the high pH observed in the soil could be attributed to the number of salts from irrigation water applied during the crop cycle (approximately 400 mm, Table 2). In addition to irrigation water, the increase in pH could result from the adding of such amendments, as observed by several authors. Eghball40, and Whalen and others41 found an increase in pH in acidic soils after the application of cattle manure, and attributed this to the presence of compounds such as Ca carbonate in the organic amendment, from animal diet (although probably bred in other production systems), and high organic acid content with carboxyl and hydroxyphenolic groups, that would help buffer the soil against changes in pH.
Although the soil values presented in this study correspond to a sampling carried out at the end of the production cycle, the K levels would indicate the need for inputs through potassium fertilization, probably due to the low K buffer power of the soil. Although the amounts of K provided by fertilizers (700 kg ha-1 of K, Table 1) and through organic amendments (165 kg ha-1 of K35, immediately available6) are high, both the quantities required (675 kg ha-1 of K) and the extracted with the harvested fruit (466 kg ha-1) are also high for a tomato crop with a yield of 150 Mg ha-1 (42. The need to adjust potassium fertilization is confirmed by Ca:K ratios greater than 30 and K:Mg ratios lower than 0.15, which suggest that deficiencies of K could be expected6.
On the other hand, no situations were detected in which the Mg indicated the probability of deficiency. This is attributed to the fact that with the average dose of mulch, 470 and 145 kg ha-1 of Ca and Mg would be applied, respectively, according to concentrations of 9.4 g kg-1 of Ca and 2.9 g kg-1 of Mg35. Apart from the contributions of Ca and Mg with amendments and irrigation water, it is common to apply these nutrients when transplanting the crop or by the leaves at fruiting (Table 1). Considering the low extraction in the fruit (17 kg ha-1 of Ca and 15 kg ha-1 of Mg)42, a large part of these nutrients would remain in the soil.
Regarding P, the high values observed in the soil are attributed to previous and recent applications of organic and inorganic sources that result in excessive amounts compared to the extracted by the crops. It is estimated that 90 kg ha-1 of P are contributed by the amendment, of which between 30 and 60% could be available the first year43. In a continuous horticultural production system in the south of the country, Docampo and others44 found that the addition of poultry manure over a period of 10 years significantly increased the available P in the soil. The values found in our study are higher than those suggested as sufficiency levels reported for demanding crops, such as alfalfa (Medicado sativa), which go around 25-30 mg kg-1, measured with P-Bray 145). The difference between the P contributions and the annual extraction by the tomato fruit harvest (30 kg ha-1 of P, according to García and Correndo42) would explain the high values of P.
The higher values of NO3 - compared to NH4 + at both depths, as well as the negative relationship between NO3 - and soil pH, indicate that there were aerobic conditions in the soil that led to the nitrification of N6. The high and positive relationship between the concentrations of NO3 - in the two depths suggests the existence of NO3 - leaching from upper strata, facilitated by the soil texture and the repeated irrigation during the crop cycle. These high levels of NO3 -detected in a deep soil sample at the end of the crop cycle constitute a risk for the environment and suggest the need to improve N management through amendments and/or fertilizers. In addition to the N applied as fertilizer, the amendments would add about 600 kg ha-1 of N, assuming a density of 0.6 g cm-3, 68% of dry matter and a total concentration of 11.5 g N kg-1(35. The amount available in the first year can vary from a quarter to about half of the total N applied in the amendment40)(41.
ec values were, in general, lower than the tolerable range indicated for moderately sensitive crops, such as Tanji and Kielen tomatoes19 (Table 2). Multiple linear regression analysis shows that Na and NO3 -contributed significantly to the ec (Table 4). Except for a very reduced number of grounds with high levels of interchangeable Na (and high pH), in general, situations that could indicate sodicity problems were not observed. Given the low concentration of Na in mulch and, assumingly, in irrigation water (conversation with J. Zamalvide; unreferenced), the accumulation of Na observed in those few cases could be attributed to low efficiency of salt leaching processes. High levels of soil pH associated with high levels of Na require monitoring the Na with specific measurements, together with the knowledge of the water composition and management, and the applied organic and inorganic sources.
5. Conclusions
The information analyzed in this study shows that the soils present high values of pH, soc and P, but, in some cases, very low K values. The fertilization management has caused excessive contributions of some nutrients (P, N, Ca, Mg) and possibly deficient management of the need for K, as well as unfavorable changes in pH and ec. It is necessary to incorporate technical criteria in fertilization management.
The high values of P suggest the need to diminish its application through fertilizers and/or organic amendments. On the contrary, regarding K, the low levels observed in some soils indicate that the potassium fertilization should be adjusted. The high values of NO3 - in the subsuperficial layer and the relations between ec, NO3 - and Na suggest that it is necessary to control both the N management and the salt leaching. This information might be relevant in developing strategies for integrated management of fertilizers and organic amendments of horticultural production systems under greenhouses.












 Curriculum ScienTI
Curriculum ScienTI